saucectl with GitHub Actions
These examples can apply to virtually any GitHub deployment, provided that you already have some existing automated tests, and are either the maintainer or an admin of the target repository.
What You'll Need
- A Sauce Labs account (Log in or sign up for a free trial license)
- Your Sauce Labs Username and Access Key
- A GitHub Account
- The following permissions in GitHub:
- ability to create and manage workflows
- ability to create and store GitHub secrets
Create GitHub Secrets
-
Export your Sauce Labs account credentials and store them as GitHub Secrets.
-
Follow the GitHub Docs to create the secrets for your repository, and add the following:
Your Sauce Username:
- Name:
SAUCE_USERNAME - Value: 'your-sauce-username'
Your Sauce Access Key:
- Name:
SAUCE_ACCESS_KEY - Value: 'your-sauce-access-key'
- Name:
Configure the GitHub Action
In your root project directory, create the following directory tree: .github/workflows. In the workflows directory create a file called actions.yml.
Add the following to the top of your file:
Setting env at the top of the file enables it globally in this workflow, so all jobs have access to these variables.
env:
SAUCE_USERNAME: ${{secrets.SAUCE_USERNAME}}
SAUCE_ACCESS_KEY: ${{secrets.SAUCE_ACCESS_KEY}}
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ github.token }}
Create the Test Job
In the examples below, we illustrate how saucectl executes tests on Sauce Cloud (i.e., Sauce Labs infrastructure).
You will likely require a tunnel back to where your app is running. A tunnel enables the remote browser to access your local network. For this, you'll need to use Sauce Connect.
For more detailed information on setting event-driven actions and jobs, visit the GitHub Action documentation.
jobs:
main:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Saucectl RUN
uses: saucelabs/saucectl-run-action@v4
with:
working-directory: v1
You can reference our example workflows in the saucectl Cypress example repository.
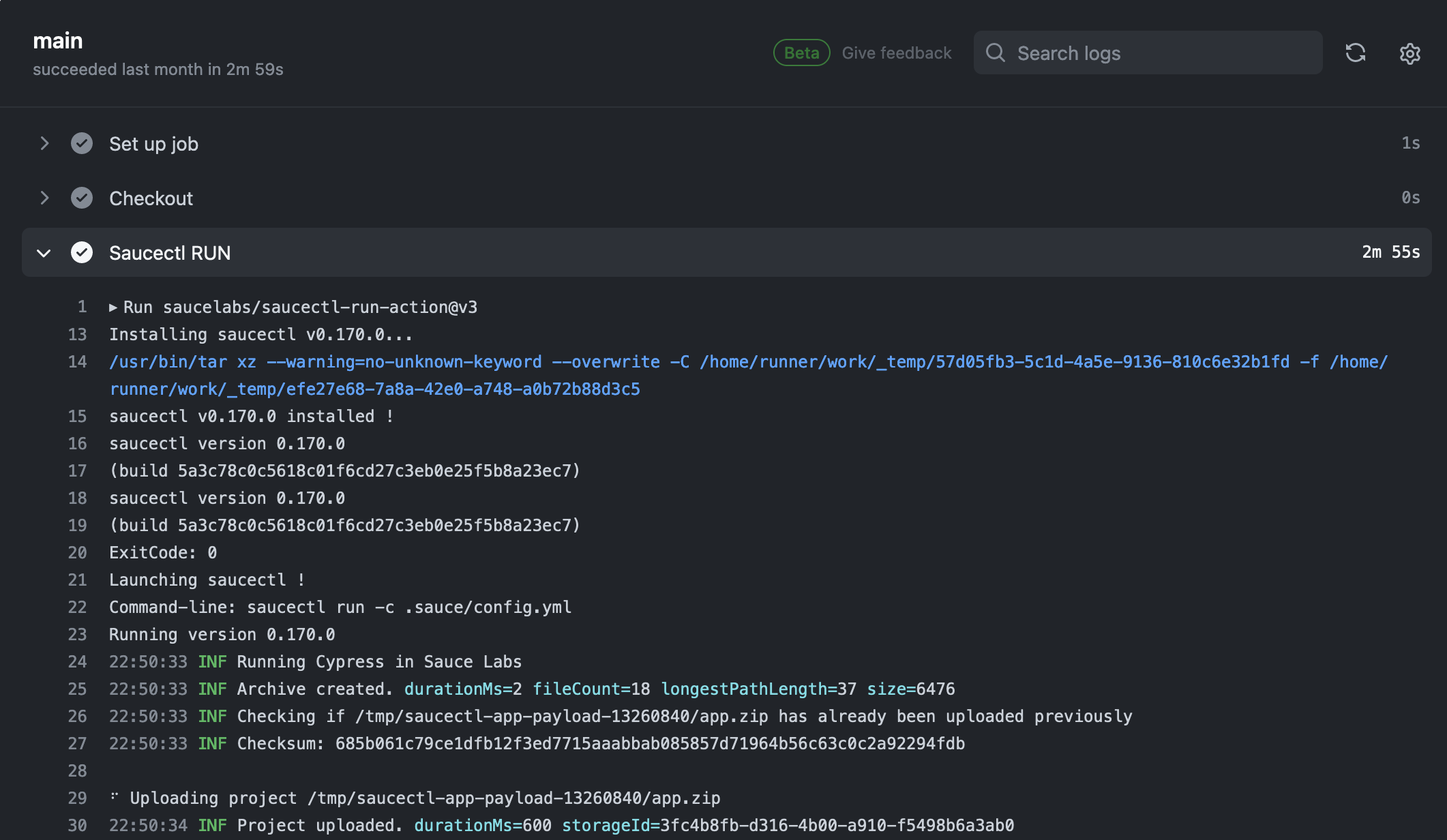
Now when you commit these files, GitHub will detect the new workflow actions and launch saucectl to run your tests.
To see the output:
-
Log in to GitHub.
-
Navigate to your repository page.
-
Click Actions.

Your output may look something like this: