Mobile App Storage
When testing mobile apps, you have the option to upload your app to our app storage. The benefits of app storage include:
- Uploading all of your mobile apps to the same location for cross-device automated and live testing with virtual devices and real devices.
- Sharing your uploaded apps with your team members.
- Sharing your uploaded apps with other teams within your organization.
- Storing apps for up to 60 days.
- App Storage supports app files in _.apk, _.aab, _.ipa, or _.zip format, up to 4GB.
Executable files (.exe) are not supported.
Make sure you have a debuggable AND non-obfuscated version of your application uploaded to Mobile App Storage to leverage all of our capabilities like Biometrics, Image injection, or Mobile App Diagnostics.
What You'll Need
- A Sauce Labs account (Log in or sign up for a free trial license).
- Your Sauce Labs Username and Access Key.
- Your mobile app file. If you don't have one on hand, consider using our Demo Apps:
Uploading Apps
Accepted File Types
App storage recognizes *.apk and *.aab files as Android apps and *.ipa or *.zip files as iOS apps. *.zip files (for Simulator tests only) are parsed to determine whether a valid *.app bundle exists.
To install an *.apk app that is extracted from an *.aab file, Sauce Labs must sign the *.apk using its own signature. In such cases, Sauce Labs signs both the app and testApp to ensure matching signatures, even if instrumentation is disabled. Otherwise, the app installation will fail. For more information, see Android App Bundles.
You can also upload and store other file types for generic use, such as a pre-run executable, package, or binary. Some of the formats for this type of use case include:
- *.js
- *.py
- *.tar
- *.zip
- *.sh
- *.bat
Sauce Labs only supports valid .zip files that can be extracted by standard unzip tools.
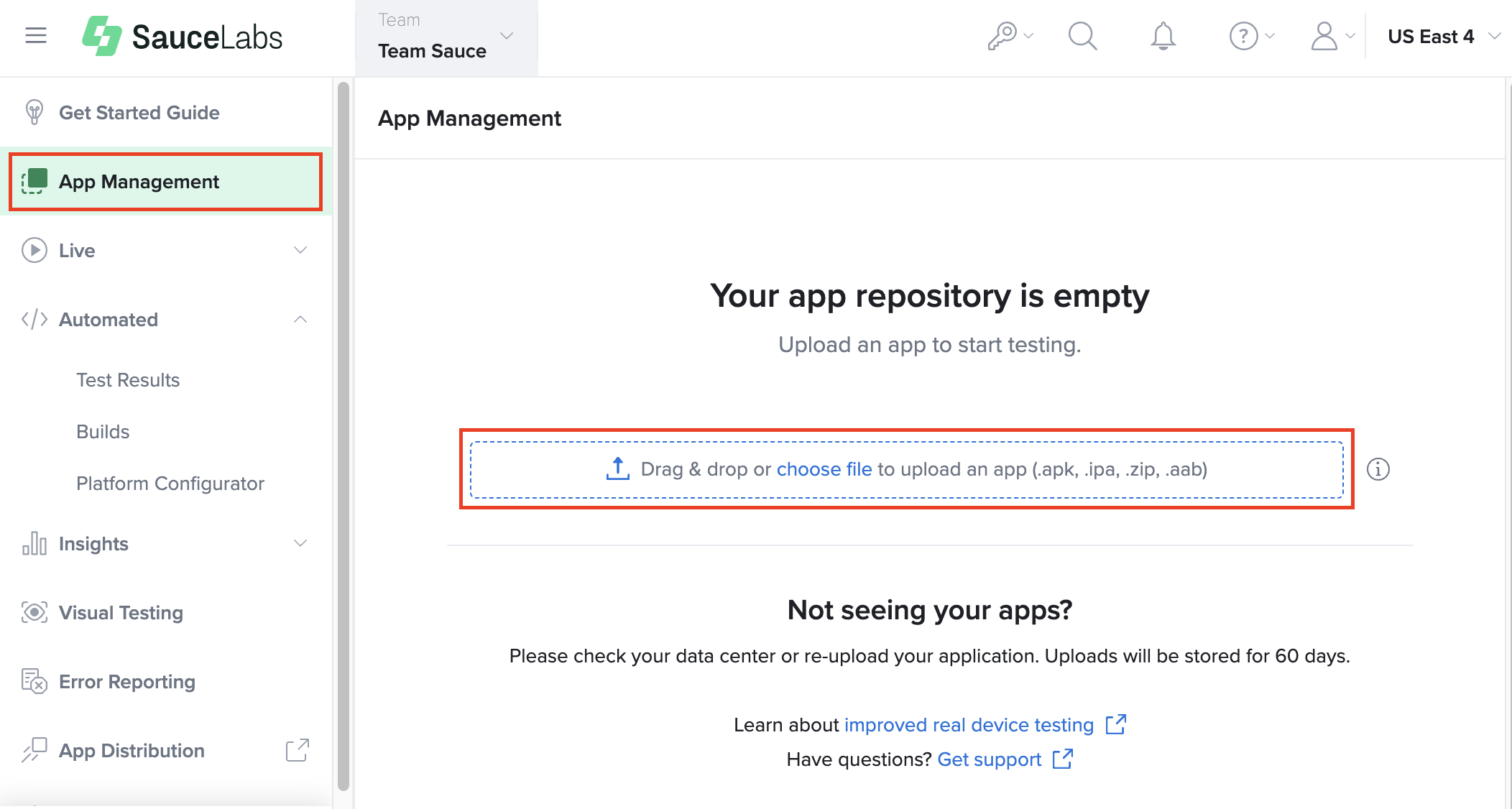
Upload Apps via UI
To upload an app via the Sauce Labs UI:
- On Sauce Labs, in the left panel, click App Management.
- To upload an app you can either drag and drop an app or browse for and select the file.
If you don't have an app to test, you can use the Sauce Labs sample mobile app.
Upload Apps via REST API
You can upload your mobile app programmatically using the File Storage API Methods. The API endpoints are Data center-specific, so make sure you are using the endpoint that is applicable for your account data center, as shown in the following example requests.
Considerations
When using the cURL sample requests below, consider the following:
- The
<path/to/your/file>variable must include the file itself, including the file extension. - The
<filename.ext>variable is the portion of the path that is just the file itself and must also include the file extension. Otherwise, the upload will succeed, but your app will not be accessible to your tests. - The
$SAUCE_USERNAME:$SAUCE_ACCESS_KEYvariable assumes you have set your Sauce Labs credentials as environment variables.
- US West
- US East
- Europe
curl -u "$SAUCE_USERNAME:$SAUCE_ACCESS_KEY" --location \
--request POST 'https://api.us-west-1.saucelabs.com/v1/storage/upload' \
--form 'payload=@"<path/to/your/file>"' \
--form 'name="<filename.ext>"'
curl -u "$SAUCE_USERNAME:$SAUCE_ACCESS_KEY" --location \
--request POST 'https://api.us-east-4.saucelabs.com/v1/storage/upload' \
--form 'payload=@"<path/to/your/file>"' \
--form 'name="<filename.ext>"'
curl -u "$SAUCE_USERNAME:$SAUCE_ACCESS_KEY" --location \
--request POST 'https://api.eu-central-1.saucelabs.com/v1/storage/upload' \
--form 'payload=@"<path/to/your/file>"' \
--form 'name="<filename.ext>"'
App Build Tags
You can add up to 10 tags to app builds either during upload or afterward using the File Storage API, providing an efficient way to organize, identify, and easily locate specific builds. Tags enable teams to label app builds by criteria such as feature, environment, or testing phase, making it faster to search and filter through multiple builds. This enhances efficiency and ensures that users can quickly find the correct build for their testing needs.
- US West
- US East
- Europe
curl -u "$SAUCE_USERNAME:$SAUCE_ACCESS_KEY" --location \
--request POST 'https://api.us-west-1.saucelabs.com/v1/storage/upload' \
--form 'payload=@"<path/to/your/file>"' \
--form 'name="<filename.ext>"' \
--form 'tags="Europe,Asia,US"'
curl -u "$SAUCE_USERNAME:$SAUCE_ACCESS_KEY" --location \
--request POST 'https://api.us-east-4.saucelabs.com/v1/storage/upload' \
--form 'payload=@"<path/to/your/file>"' \
--form 'name="<filename.ext>"' \
--form 'tags="Europe,Asia,US"'
curl -u "$SAUCE_USERNAME:$SAUCE_ACCESS_KEY" --location \
--request POST 'https://api.eu-central-1.saucelabs.com/v1/storage/upload' \
--form 'payload=@"<path/to/your/file>"' \
--form 'name="<filename.ext>"' \
--form 'tags="Europe,Asia,US"'
Rate Limiting
To increase service stability and prevent overload by a high volume of incoming traffic, we have set the following rate limits for uploading your mobile apps (effective from November 14th, 2022):
| Trial Users | Non Trial Users | |
|---|---|---|
| Uploads |
|
|
Access Restriction
Team Restriction
All uploaded files are shared within the same team, and members can only access files available to the active team they belong to. Organization admins have access to all files across the organization.
For more information about managing access to your organization, see Managing User Information.
Share Apps with another Team
App groups can be shared across teams within an organization, but only organization admins have the permission to share an app group with other teams.
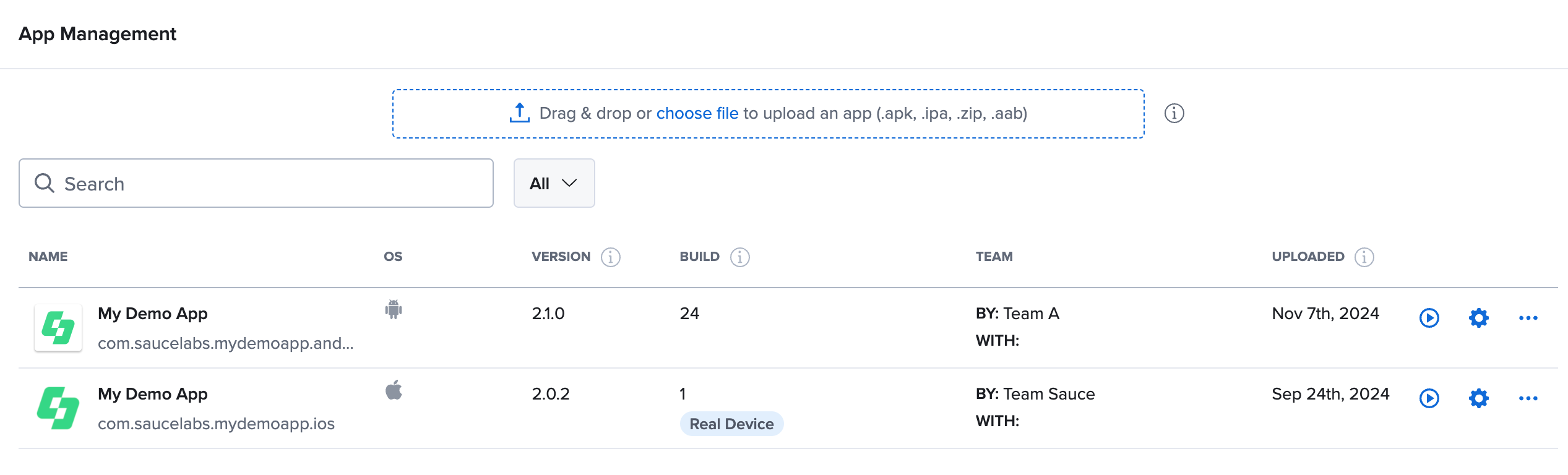
Shared apps will appear under the Shared With Me tab on the App Management page for non-organization admins, and team members can use these apps just as they would with apps from their own team. However, teams with a shared app group cannot delete it, ensuring the app remains accessible to all assigned teams.
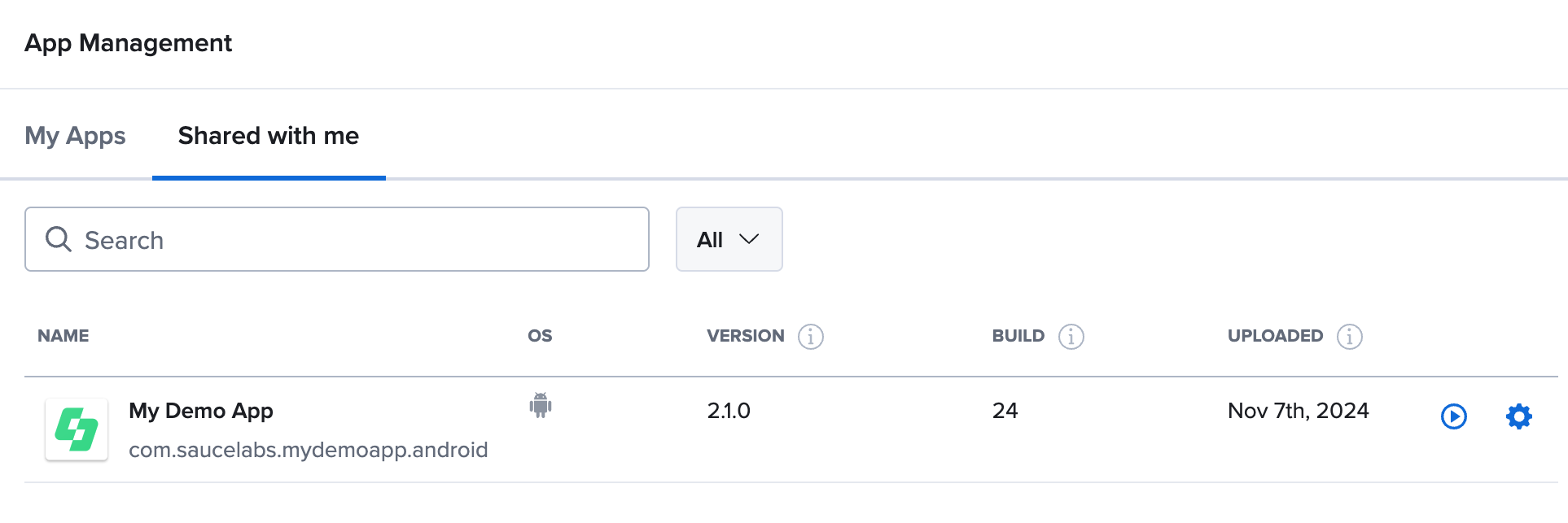
Share an App Group
- Navigate to App Management and click on More Actions on the app group row you want to share.
- Select Share to open the Share Modal.
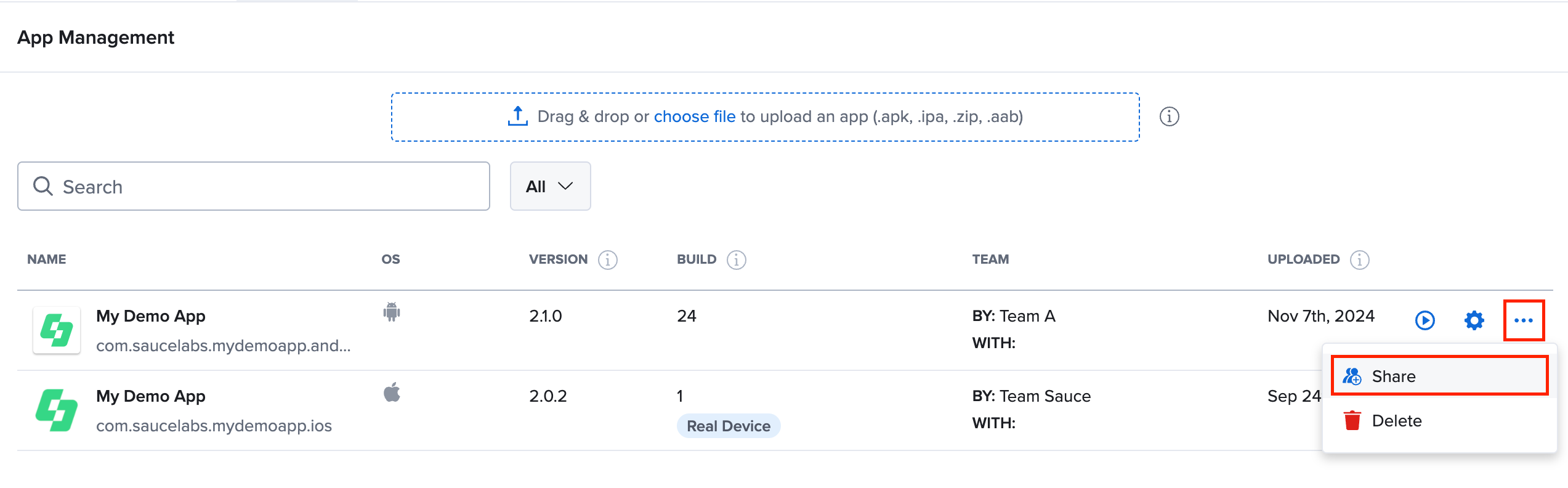
- From the dropdown list, choose the teams you want to share the app group with.
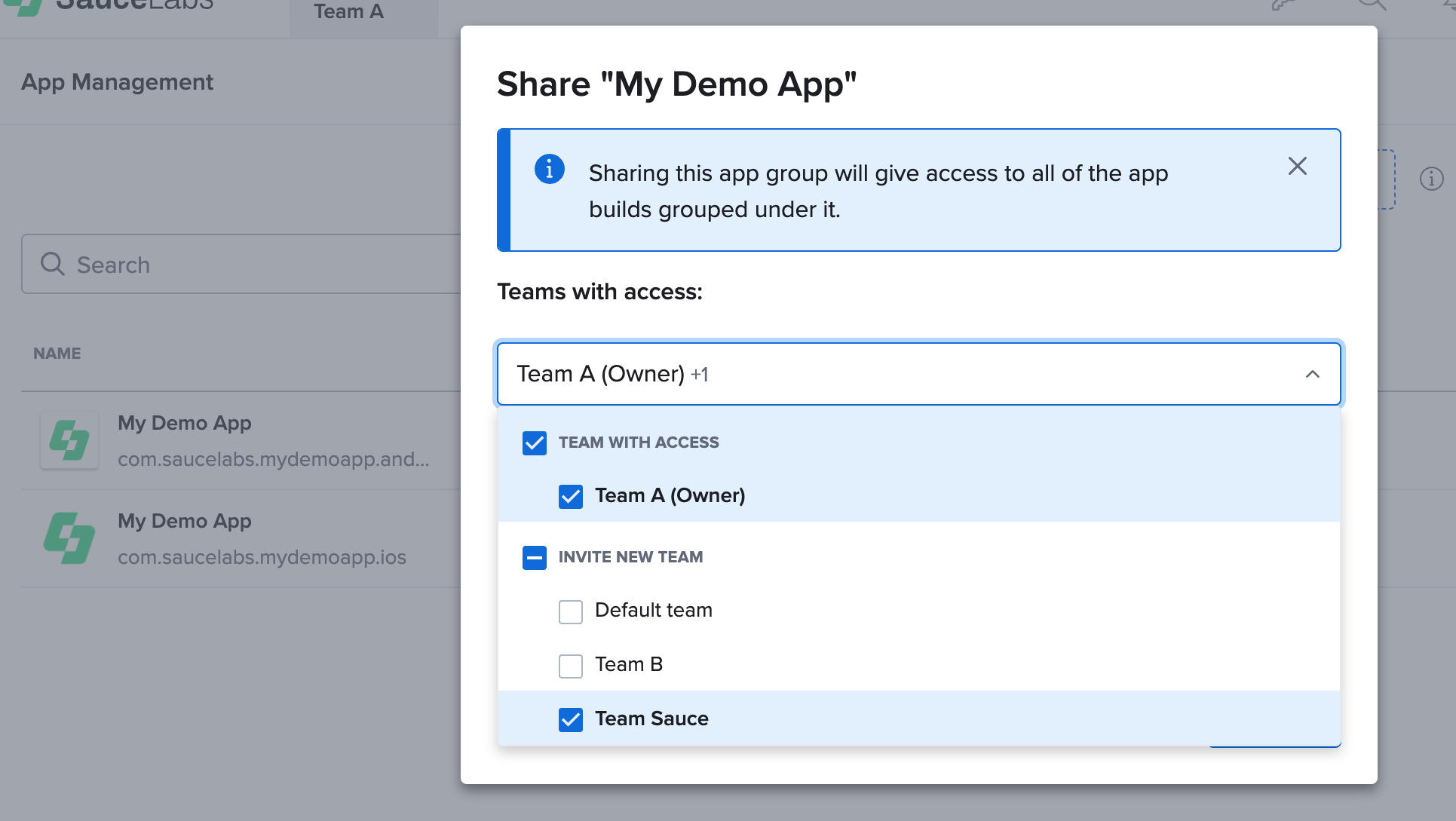
- The new team selection will replace all previously shared teams, so review the table below to ensure the correct teams have access.
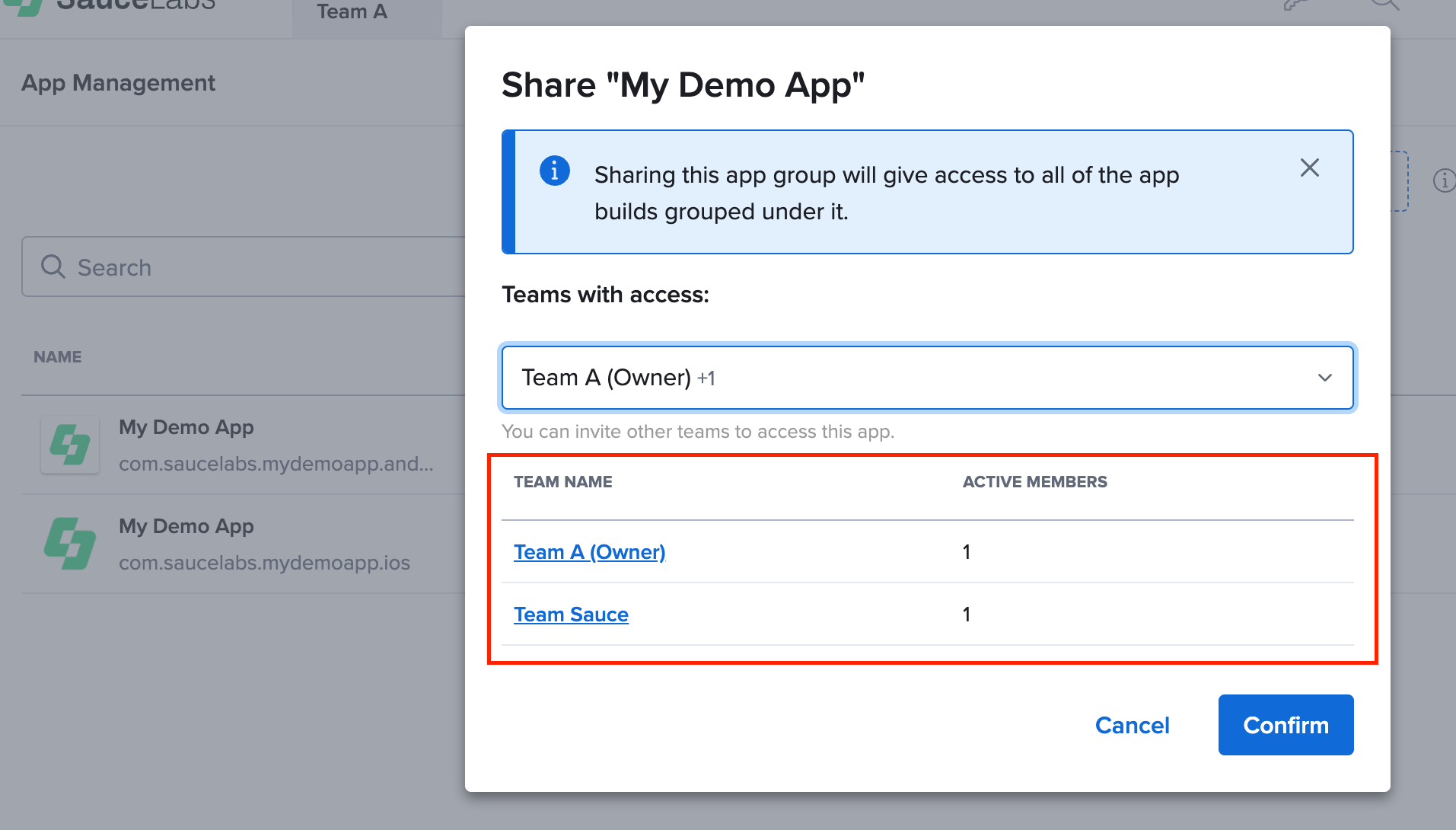
- Click Confirm to share the app with the selected teams.
App Management
To view all app builds under one app group or change the app settings, on the App Management page, hover over the app and then click Settings and App Versions.
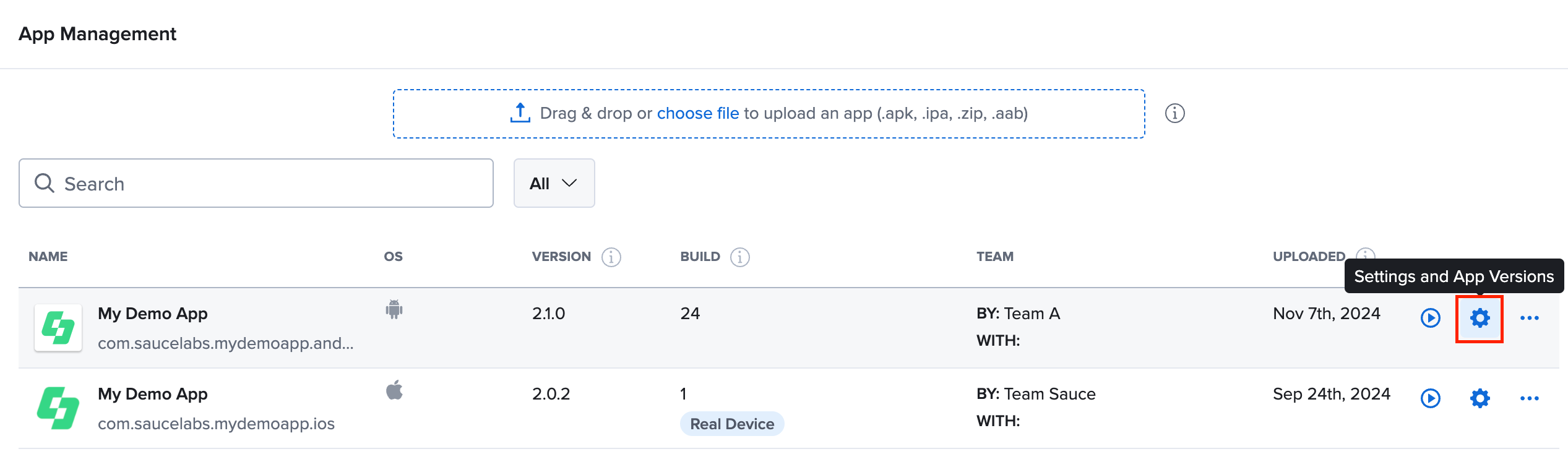
The version number shown is the most recently uploaded file, not necessarily the latest version of the app. Deleting an app in Sauce Labs will delete the whole app group (i.e., the group of builds belonging to the same app package).
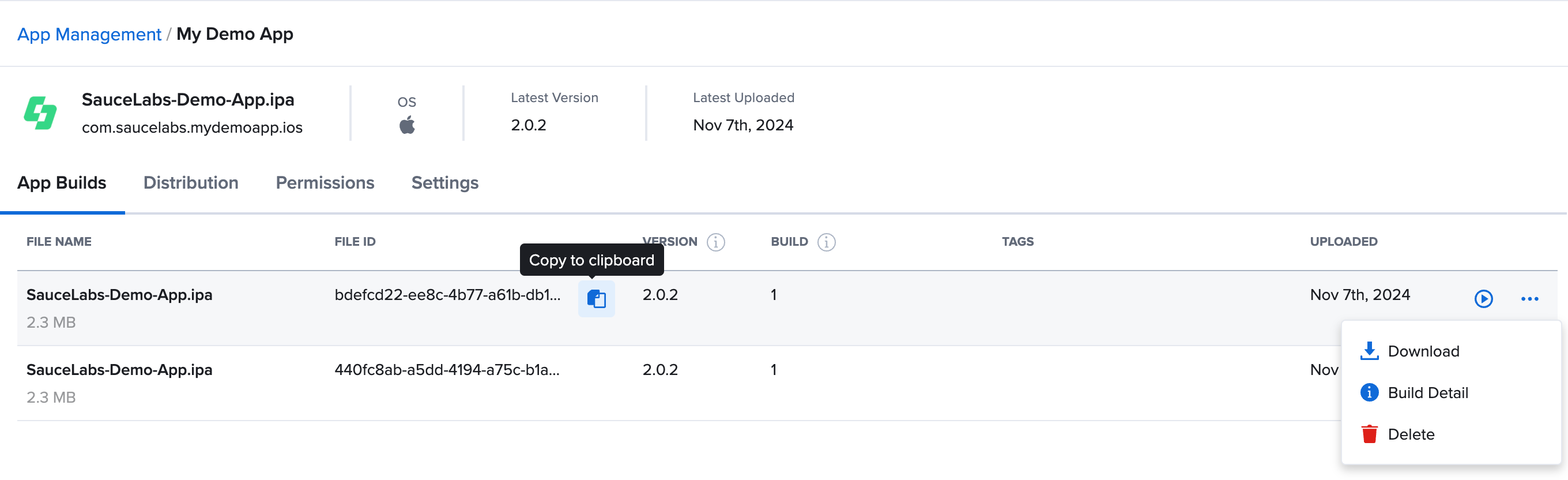
App Builds
The App Builds tab displays a table of all app builds within the selected app group. To quickly copy an app's file name or ID, hover over the app and click the clipboard icon. Available actions include starting a test, downloading the app build, and viewing build details. Deleting an app build is restricted to organization and team admins.
Distribution
Distribute your app to internal and external beta testers through Sauce Labs Mobile App Distribution to gain early feedback before production. Learn more about app distribution powered by Sauce Labs Mobile App Distribution.
Permissions
Coming soon
We're building a new permission system for admins to control who can upload, delete, modify settings, and run tests on apps. It will boost flexibility and security, ensuring that only authorized users can manage key features.
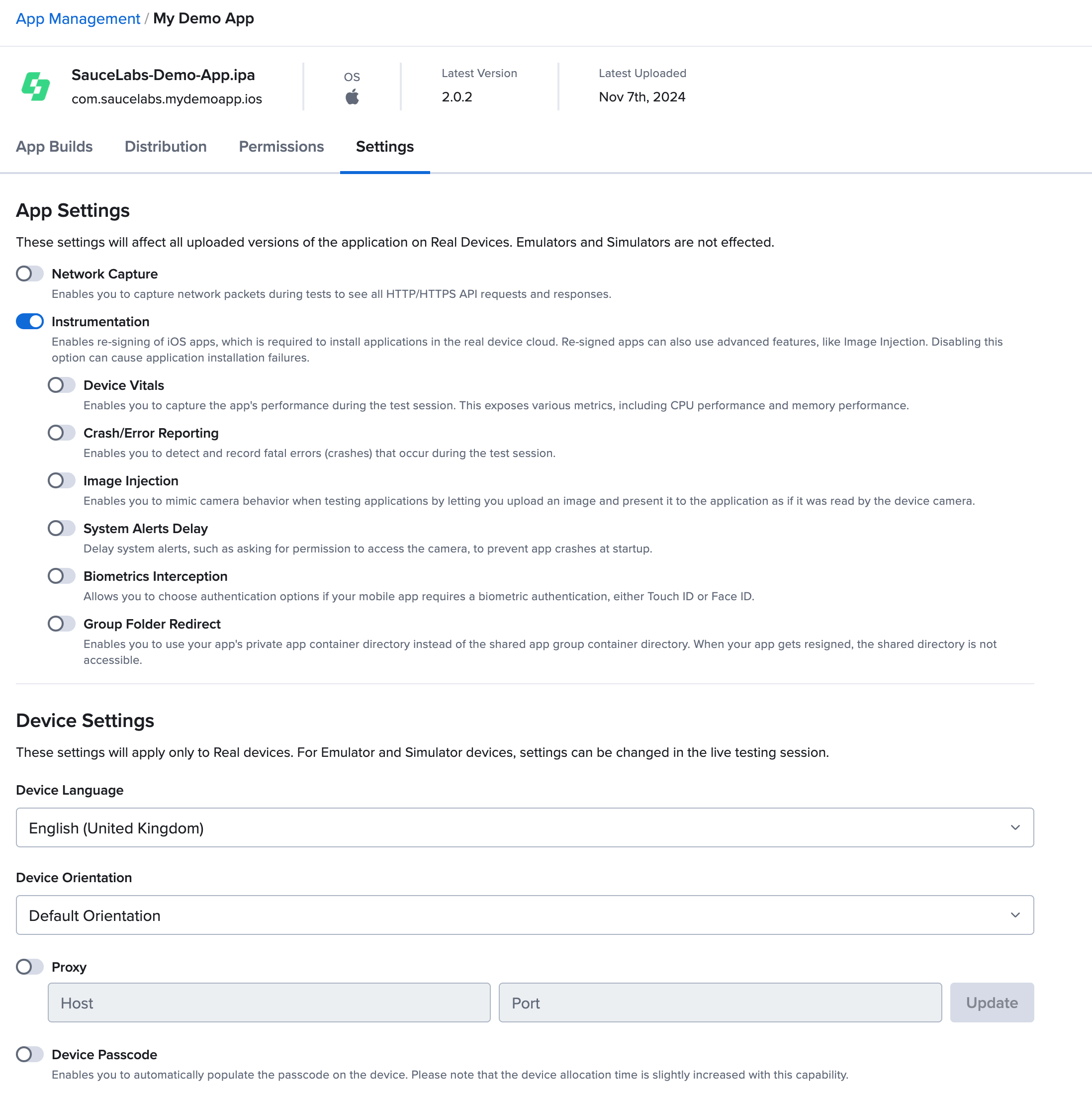
Settings
A range of device and app settings can be configured to serve as the default for both manual and automated test runs on real devices. Only organization and team admins have permission to modify these settings.
For more information about managing your device and app settings, see Real Device Settings.
Using App Storage with Automated Test Builds
After successfully uploading your file to app storage, you need to reference the unique app Identifier (file_id) in your test code to retrieve and use your app for automated tests.
For example, let's assume you've updated a new version of your app using the /upload endpoint. The JSON response would be something like:
{
"item":{
"id":"379c301a-199c-4b40-ad45-4a95e5f30a3a",
"owner":{
"id":"286c0fbb0cb644c4a012d505b8a0a1ac",
"org_id":"c064890612424e34a12fca98ce4f32c6"
},
"name":"Android.SauceLabs.Mobile.Sample.app.2.3.0.apk",
"upload_timestamp":1593450387,
"etag":"0cf189b1c4c17a56656ada5e2d75cd51",
"kind":"android",
"group_id":2807,
"metadata":{
"identifier":"com.swaglabsmobileapp",
"name":"Swag Labs Mobile App",
"version":"2.3.0",
"icon":"<long-serial-number>",
"version_code":13,
"min_sdk":16,
"target_sdk":28
},
...
}
}
}
Then the file_id would be "id":"379c301a-199c-4b40-ad45-4a95e5f30a3a". If you're unsure of the id of an existing app, you can use the Storage API to look up the file id of an app in the storage or check out the App Builds in the UI.
File Name instead of File ID
You can also use the app name field from the storage API in the app capability. This approach is particularly useful if you upload your build to app storage via a CI pipeline, and you either don't know the id, or you do not wish to perform JSON parsing to retrieve the id. The filename field also includes any supported file that can be uploaded to app storage.
Example of uploading an Android .apk file:
- Java
- JS
- Python
- Ruby
- C#
caps.setCapability("app", "storage:filename=<file-name>.apk");
caps['app'] = 'storage:filename=<file-name>.apk';
caps['app'] = "storage:filename=<file-name>.apk"
caps['app'] = 'storage:filename=<file-name>.apk'
caps.SetCapability("app","storage:filename=<file-name>.apk");
Limitations
- File names are NOT unique, therefore they will always default to the latest version.
- Currently, you cannot specify the version of the app using this feature.
buildcapability is not supported in VDC at this time.
Example Code
These examples assume file_id = c8511dd6-38ec-4f58-b8b9-4ec8c23ad882
- Java
- JS
- Python
- Ruby
- C#
caps.setCapability("app", "sauce-storage:some-app.apk");
caps.setCapability("app", "storage:c8511dd6-38ec-4f58-b8b9-4ec8c23ad882");
caps['app'] = 'sauce-storage:my_app.apk';
caps['app'] = 'storage:c8511dd6-38ec-4f58-b8b9-4ec8c23ad882';
caps['app'] = "sauce-storage:my_app.apk"
caps['app'] = "storage:c8511dd6-38ec-4f58-b8b9-4ec8c23ad882"
caps['app'] = 'sauce-storage:my_app.apk'
caps['app'] = 'storage:c8511dd6-38ec-4f58-b8b9-4ec8c23ad882'
caps.SetCapability("app","sauce-storage:my_app.apk");
caps.SetCapability("app","storage:c8511dd6-38ec-4f58-b8b9-4ec8c23ad882");
Using Dependent Apps for a Test
Real Devices OnlyIf your real device testing requires your app under test to have access to other apps and you, therefore, need to install those dependent apps and reference them in your tests, you can do so using the otherApps capability.
Dependent apps inherit the configuration of the main app under test for Device Language, Device Orientation, and Proxy, regardless of what settings may have been applied to the app at the time of upload, because the settings are specific to the device under test. For example, if the dependent app is intended to run in landscape orientation, but the main app is set to portrait, the dependent app will run in portrait for the test, which may have unintended consequences.
Appium Capability
For Appium
tests, you can specify up to seven apps that have already been uploaded to App
Storage using one of the previously described methods by setting the otherApps
desired capability and referencing the app's storage ID or filename.
caps.setCapability("otherApps", "storage:filename=<file-name>")
caps.setCapability("otherApps", "storage:<fileId>")
- Android dependent apps will not be instrumented or modified.
- iOS dependent apps will always be resigned/modified (even when resigning is disabled for the main app) because apps can't be installed on iOS devices without resigning them. If a dependent app cannot be resigned (such as a 3rd party app), the test will not work as intended.
Espresso/XCUITest Configuration
For Espresso or XCUITest testing, you can specify up to seven dependent apps to either upload from your local machine or that are already in App Storage. In your saucectl configuration file, specify a local filepath (relative location is {project-root}/apps/app1.apk) or an expanded environment variable representing the path, and saucectl will upload the app to App Storage for use with the test. Otherwise, specify an app in App Storage using the reference storage:<fileId> or storage:filename=<filename>.
espresso:
otherApps:
- ./apps/pre-installed-app1.apk
- $PRE_INSTALLED_APP2
- storage:c78ec45e-ea3e-ac6a-b094-00364171addb
- storage:filename=pre-installed-app3.apk
Installing Apps from a Remote Location
Real Devices Only
If your app is downloadable from a remote location (for example, AWS S3 bucket, a GitHub repository), you can provide a URL as the value for the app capability in your test, which will install the app onto the real devices prior to test execution.
Appium cannot log in to secure locations, so apps installed via remote download must be accessible, so are then removed from the real device immediately following test completion, providing an added layer of security.
To install a remote app on a real device for a test:
- Make sure the app meets the requirements for Android and iOS Mobile App Testing.
- Ensure Sauce Labs has READ access to the app URL.
- In your Appium test script, enter the app file location URL as the
appdesired capability:
caps.setCapability("app", "https://github.com/saucelabs/sample-app-mobile/releases/download/2.3.0/Android.SauceLabs.Mobile.Sample.app.2.3.0.apk?raw=true");
Android:
- The Instrumentation feature will not work if the app is installed from an external location.
iOS:
- The app cannot be installed on public devices due to signing.
- The app can be installed on private devices. However, to make this work you must add the UDID of the private device to the provisioning profile for iOS (see our resigning process to learn more).
- The Instrumentation feature will not work if the app is installed from external location.
Deprecated Sauce-Storage
If you were previously using apps stored in sauce-storage, you can convert your existing test capabilities by replacing sauce-storage:myapp with storage:<file_id>.