Crashpad Integration Guide for Visual Studio 2022
(C++ and Crashpad)
Follow these steps to add Crashpad to a C++ project.
Build Crashpad binaries
In a x64 Native Tools Command Prompt for VS 2022 run the following commands to build Crashpad binaries for both the Debug and Release configurations.
git clone https://github.com/backtrace-labs/crashpad.git
cd crashpad
cmake -B cbuild
cmake --build cbuild --config Debug
cmake --build cbuild --config Release
Set up a Visual Studio project
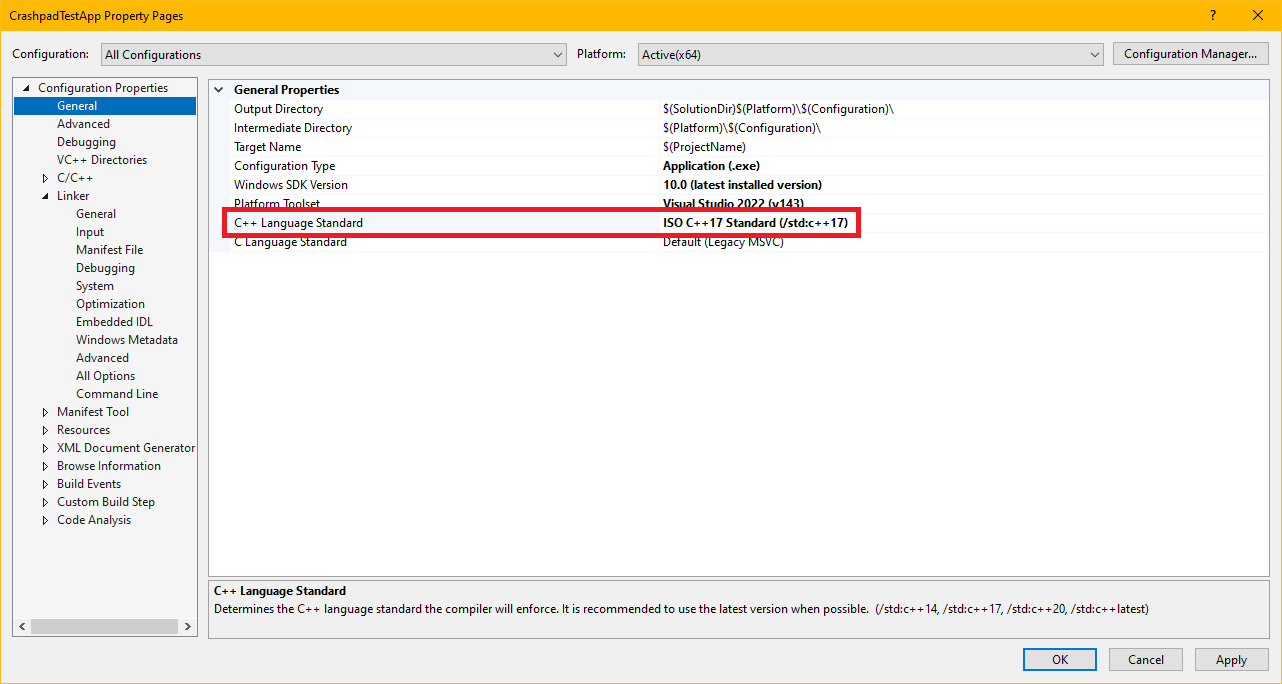
Set Language Standard
Crashpad requires C++20. In project properties, select All Configurations and change the C++ Language Standard in the General tab from the default C++14 to C++20 (/std:c++20), if necessary.
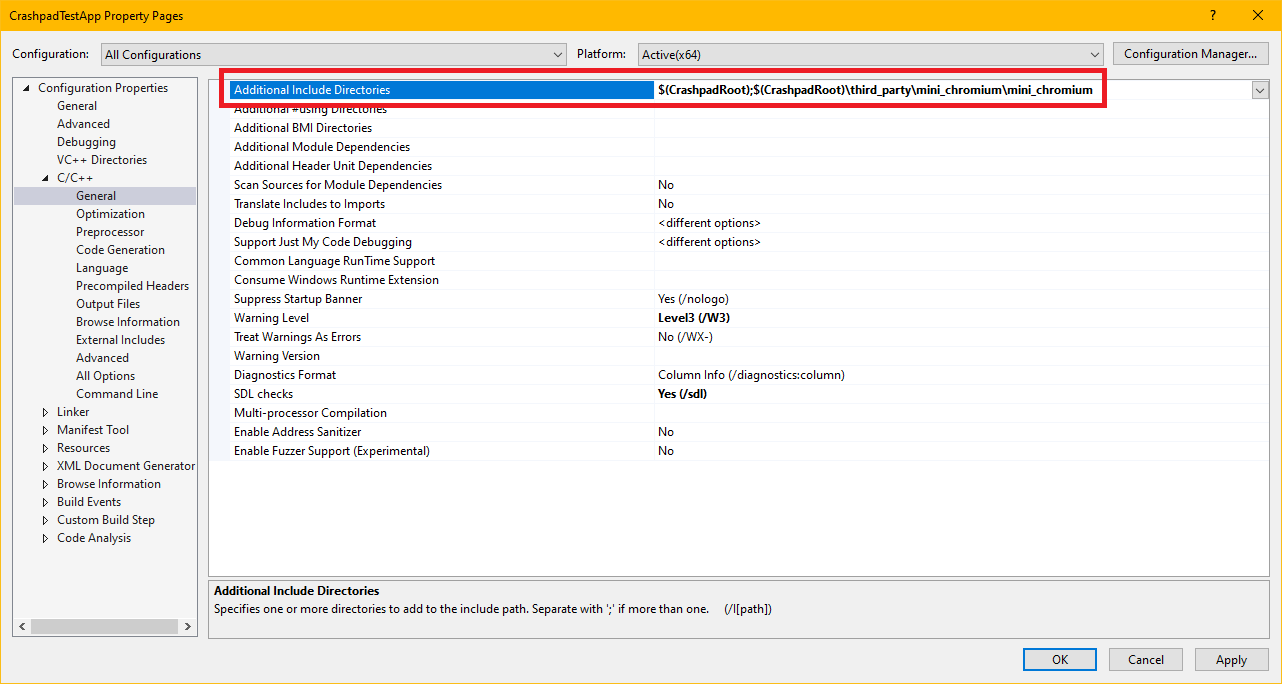
Set Additional Include Directories
To simplify the paths, the following instructions assume that $(CrashpadRoot) is defined in a property sheet and points to the root directory of the cloned Backtrace Crashpad source code from the previous step.
Add the following include directories in your Visual Studio project for all configurations in C/C++, Additional Include Directories:
$(CrashpadRoot)$(CrashpadRoot)\third_party\mini_chromium\mini_chromium
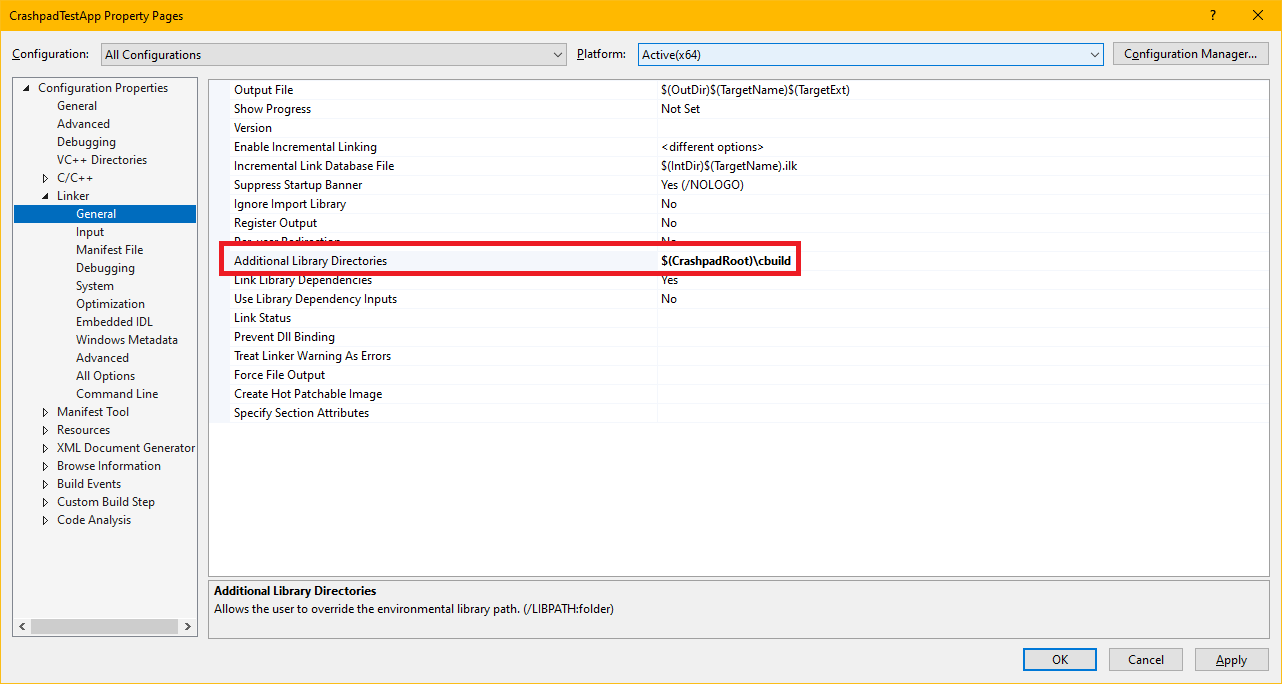
Set Additional Library Directory
Add a library directory pointing to the build output directory from the previous step in the project's Linker, General, Additional Library Directories. This would be $(CrashpadRoot)\cbuild, for instance.
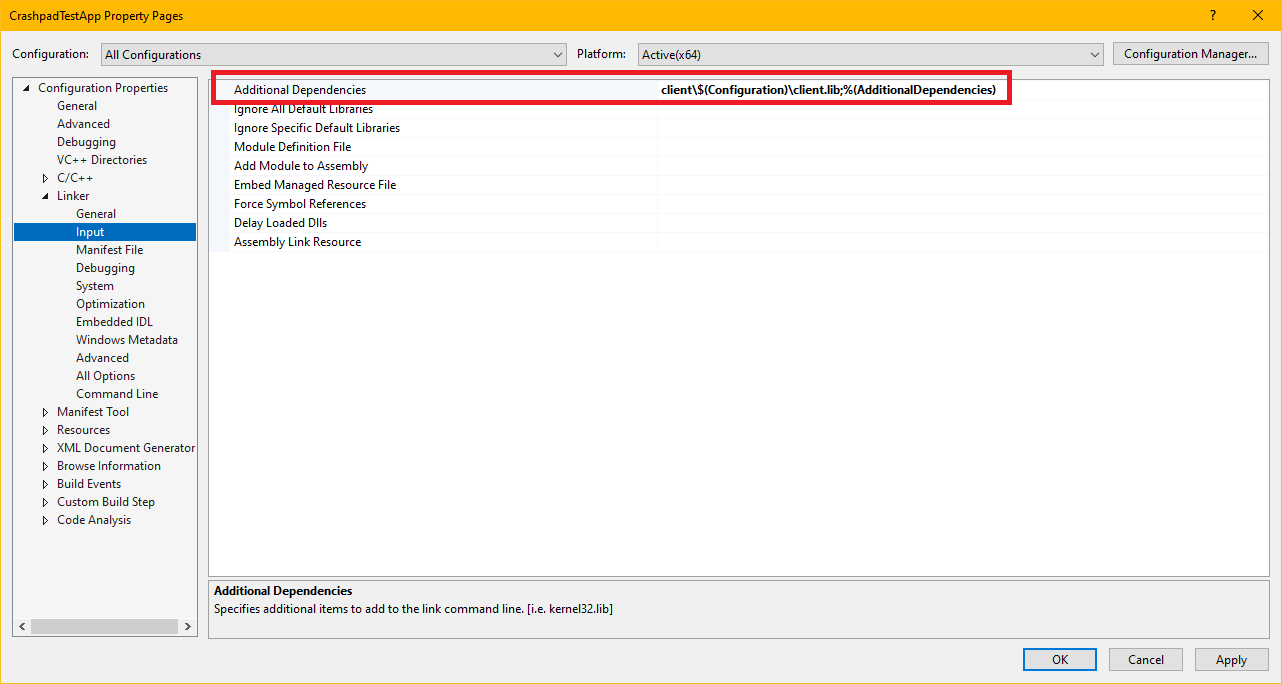
Add Additional Library Dependencies
Add the following libraries in the project's Linker, Input, Additional Dependencies.
For debug configuration(s):
client\Debug\client.lib
For release configuration(s):
client\Release\client.lib
Or, if the configurations are named Debug and Release then this can be simplified to the following for all configurations:
client\$(Configuration)\client.lib
Ensure Symbol Generation
It is required to upload symbols into Backtrace for intelligent deduplication and classification. This section explains how to enable debug symbols for your application.
For Windows, Go to Project > Properties > Linker and update the Generate Debug Info setting. You'll want to set it to Generate Debug Information optimized for sharing and publishing (/DEBUG:FULL).
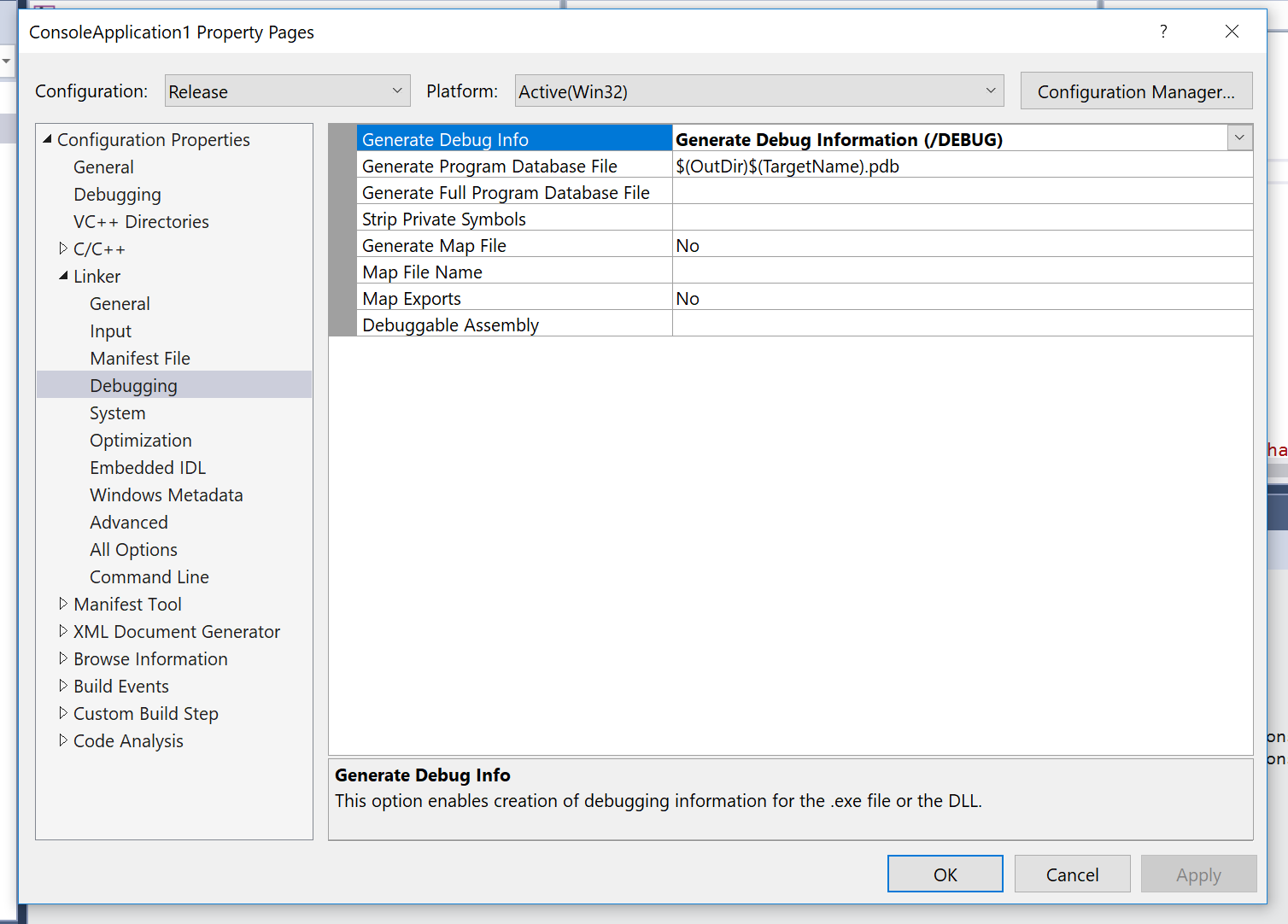
This setting generates a .pdb file for your application in the build output directory. You can manually upload .sym, .pdb, and archive files containing .pdb or .sym files into Backtrace or through the command line. It is also possible to hook up Visual Studio to automatically upload symbols as they are generated. Be sure to upload the corresponding .dll or .exe along with the .pdb.
Alternative Integration
Pre-built Binaries
To use the prebuilt static library and handler from GitHub follow these steps.
Because crashpad is built in CI as a static library against a single version of Visual Studio there are no guarantees that the library is compatible with later (or even different) versions of Visual Studio. It is recommended to build the distribution, as documented above, against your specific toolchain for debug and release configurations for maximum compatibilty.
Extract the Visual Studio build from releases to your project's third_party\crashpad directory.
Set Additional Include Directories
Add the following include directories in your Visual Studio project for all configurations in C/C++, Additional Include Directories:
third_party\crashpad\include
Add Additional Library Dependencies
Add the following libraries in the project's Linker, Input, Additional Dependencies for all configurations
third-party\crashpad\bin\client.lib
Code Samples
For either integration documented above, the following code can be added to your project and can be used to initialize Crashpad in your application.
Header, bt_crashpad.h
#pragma once
namespace backtrace {
bool startCrashHandler();
}
Source file, bt_crashpad.cpp
#include "bt_crashpad.h"
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <memory>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#define NOMINMAX // prevent Windows headers from defining min/max
#include <client/crash_report_database.h>
#include <client/settings.h>
#include <client/crashpad_client.h>
#include <client/crashpad_info.h>
/*
* ENSURE THIS VALUE IS CORRECT.
*
* This is the directory used to store and queue crash data for the application.
*/
static const wchar_t CRASHPAD_DATABASE_PATH[] = L".";
/*
* ENSURE THIS VALUE IS CORRECT.
*
* Crashpad has the ability to support crashes both in-process and out-of-process.
* The out-of-process handler is significantly more robust than traditional in-process
* crash handlers. This path may be relative. Point to the installed Crashpad handler
* built from the Backtrace Crashpad source.
*/
static const wchar_t CRASHPAD_HANDLER_PATH[] = L".\\handler.exe";
/*
* YOU MUST CHANGE THIS VALUE.
*
* Replace "youruniverse" with the Backtrace universe name and replace the submission token.
*/
static const char BACKTRACE_SUBMIT_URL[] = "https://submit.backtrace.io/youruniverse/000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000/minidump";
namespace backtrace {
static std::unique_ptr<crashpad::CrashReportDatabase> database;
bool startCrashHandler()
{
using namespace crashpad;
std::map<std::string, std::string> annotations;
std::vector<std::string> arguments = { "--no-rate-limit" };
/*
* THE FOLLOWING ANNOTATIONS MUST BE SET.
*
* Backtrace supports many file formats. Set format to minidump
* so it knows how to process the incoming dump.
*/
annotations["format"] = "minidump";
base::FilePath db(CRASHPAD_DATABASE_PATH);
base::FilePath handler(CRASHPAD_HANDLER_PATH);
database = crashpad::CrashReportDatabase::Initialize(db);
if (database == nullptr || database->GetSettings() == NULL)
return false;
/* Enable automated uploads. */
database->GetSettings()->SetUploadsEnabled(true);
return CrashpadClient{}.StartHandler(
handler, db, db, BACKTRACE_SUBMIT_URL, annotations, arguments, false, false, {}
);
}
}
In your initialization code,
#include “bt_crashpad.h”
{
…
if (backtrace::startCrashHandler() == false)
{
// crashpad failed to start
}
…
}