Writing API Tests with the Composer
The API Testing Composer enables you to quickly generate API functional tests (no coding experience required) and/or code them from scratch. You can reuse these tests as end-to-end integration tests and load (stress) tests. In turn, load tests can be reused as monitors for performance testing.
What You'll Need
- A Sauce Labs account (Log in or sign up for a free trial license).
- An existing API Testing Project. For details on how to create one, see API Testing Quickstart.
Creating a Test with the Composer
Create a Test
- In Sauce Labs, click API Testing.
-
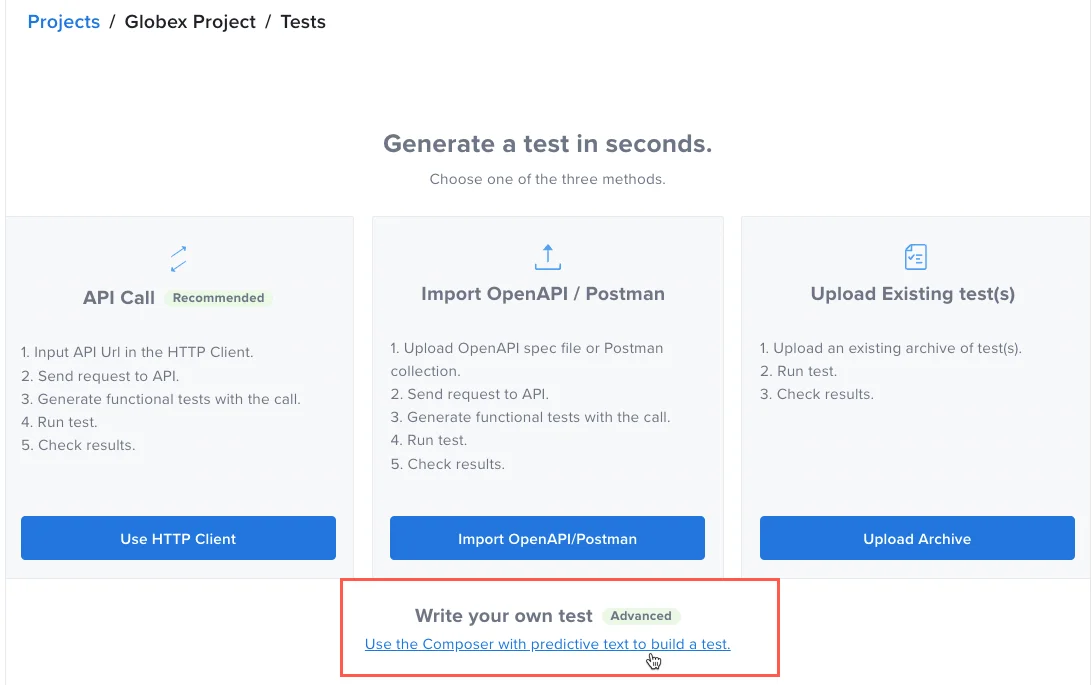
On the Projects page:
- If you have no tests or projects yet, in the Write your own test box, click Use Composer.
-
If you have a project but no tests, on the Projects page, click Write your own test.
-
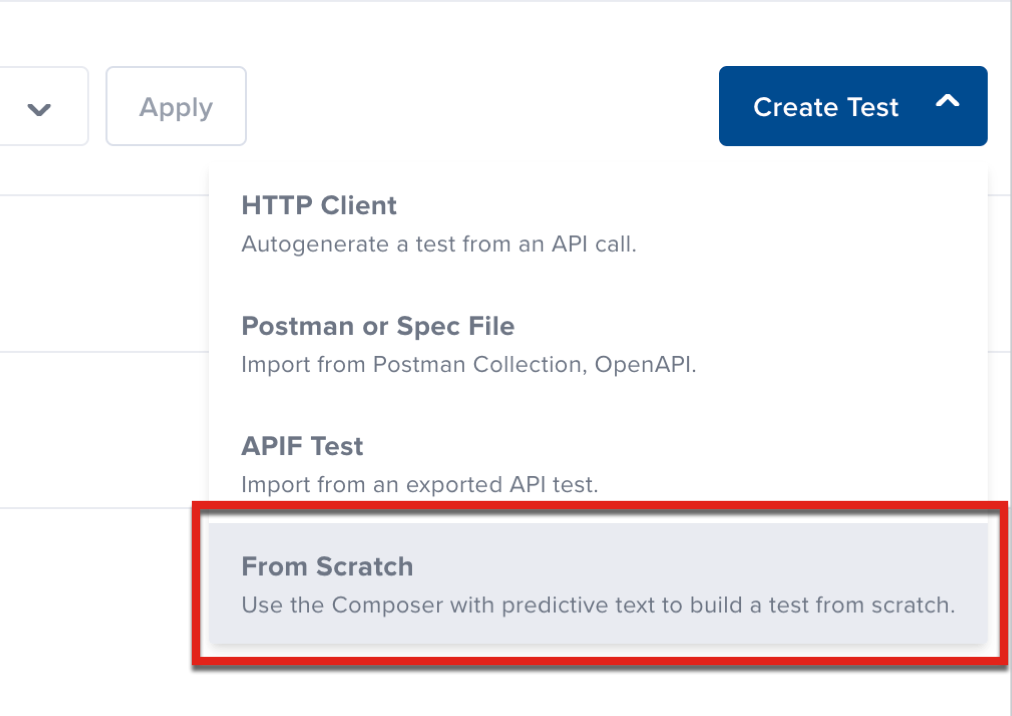
If your project has tests, click Create Test and then click From Scratch.
-
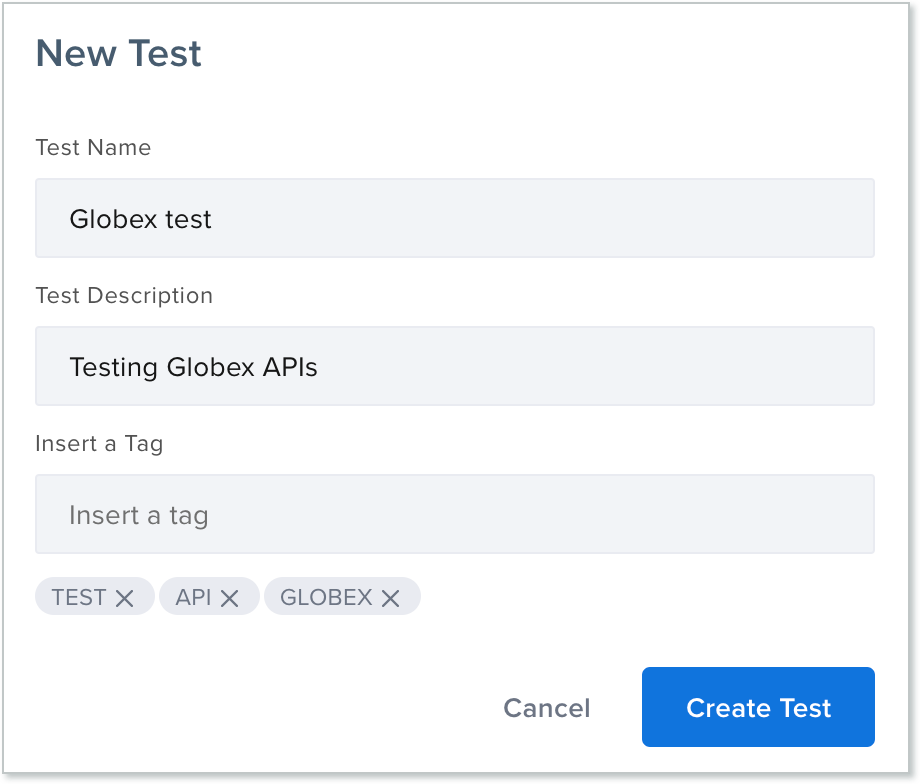
In the New Test box, enter a test name, test description (optional), and tags (optional), and then click Create Test.
You can use either the Visual composer (guides you through building components, with no coding required) or the Code composer (requires you to write code from scratch). For this guide, we're using Visual.
For more information, see Input Sets and Visual View and Code View.
Add Test Components
When test components are combined, they act as our test logic. See the following pages for more information about the components types available in API Testing:
Add an I/O Request Test Component
To create a simple GET request and validate that response is correct:
- In API Testing, on the Compose page, click Add child component.
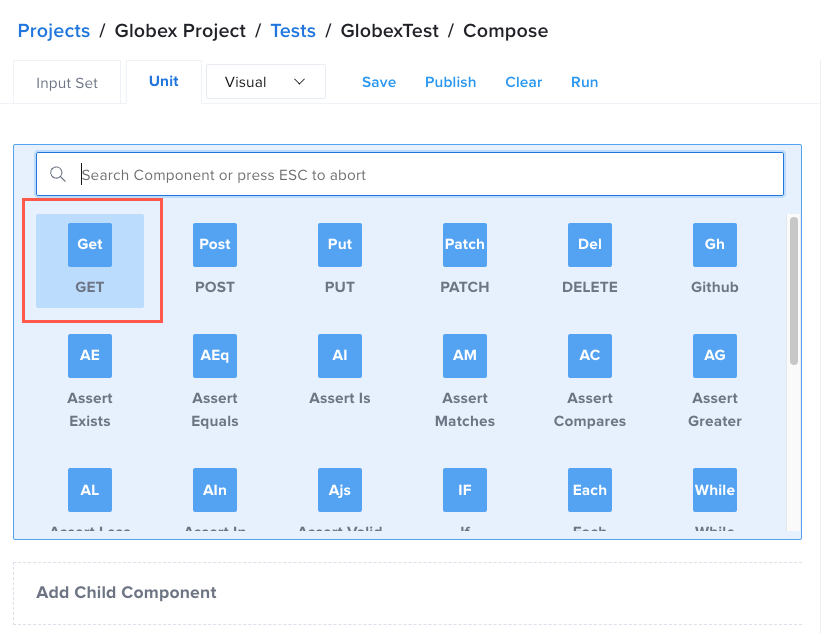
- In the list of component options, click the GET component.
-
In the GET request window, in the Url field, enter
https://api.us-west-1.saucelabs.com/rest/v1/public/tunnels/info/versions. This endpoint will return a JSON response body. -
In the Variable field, enter payload. This variable stores the response, so it can now be referred to as payload.
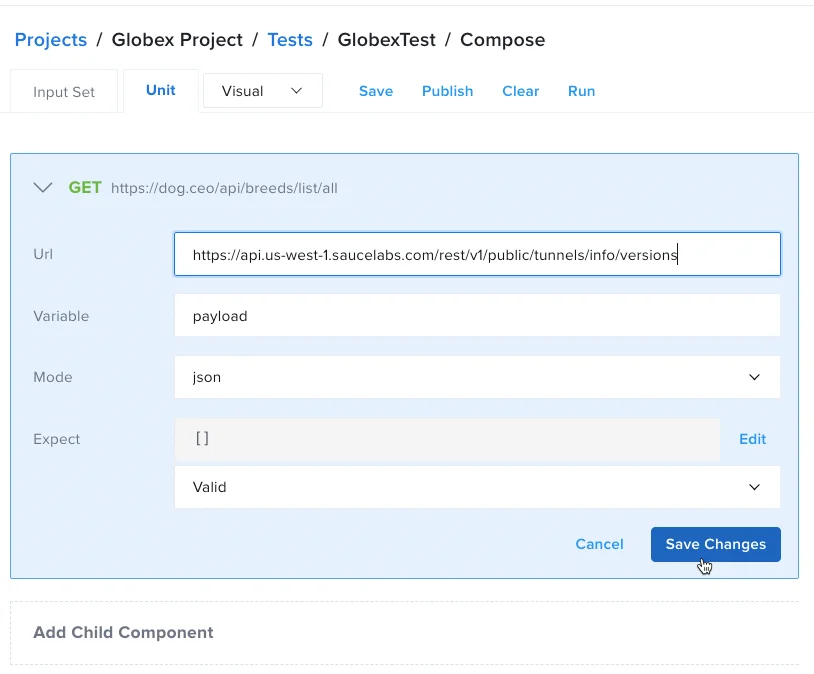
- Leave the rest of the fields blank and then click Save Changes.
The result should look like the following:
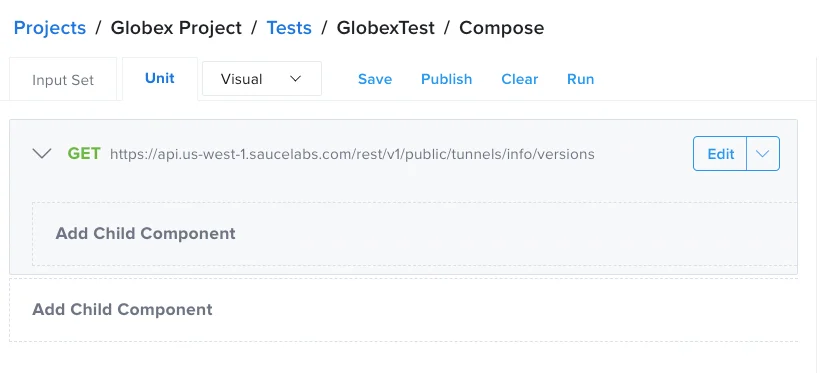
For more information, see I/O Request Test Components.
Add an Assertion Component
- In API Testing, on the Compose page, click Add child component.

- In the list of component options, click the Assert Exists component.
-
In the Assert exists window, in the Expression field, enter
payload.downloads. This expression checks for the downloads field in the json response body. -
Leave the rest of the fields blank and click Save Changes.
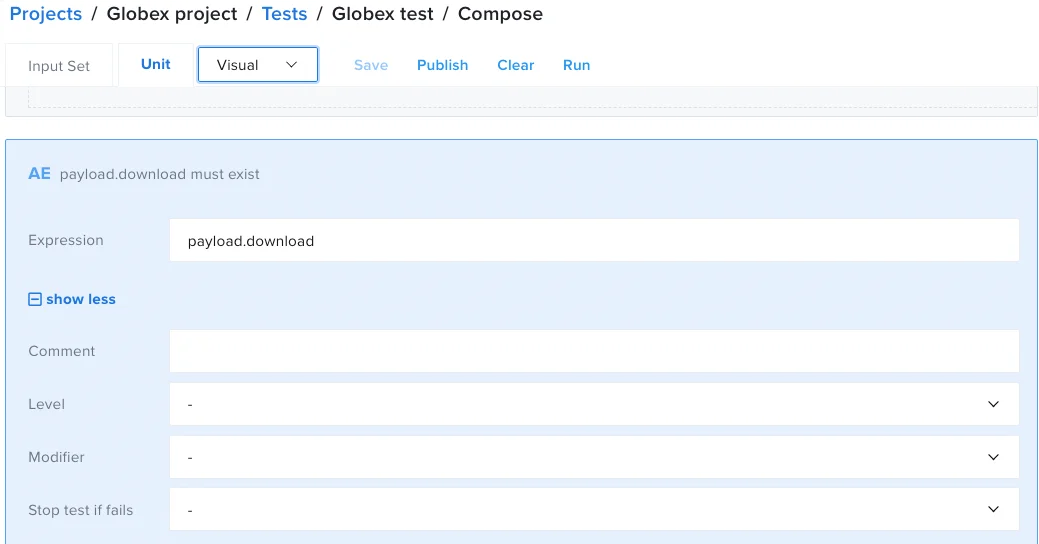
- The result should look like the following:

For more information, see Assertion Test Components.
Additional Example
In the following example, the expression checks if the download_url value inside the Linux object is a valid URL.
-
In API Testing, on the Compose page, click Add child component.
-
In the list of component options, click the Assert Is component.
-
In the Assert is window, in the Expression field, enter
payload.downloads.linux.download_url. This expression checks for the download_url field in the json response payload. -
Leave the rest of the fields blank and click Save Changes.
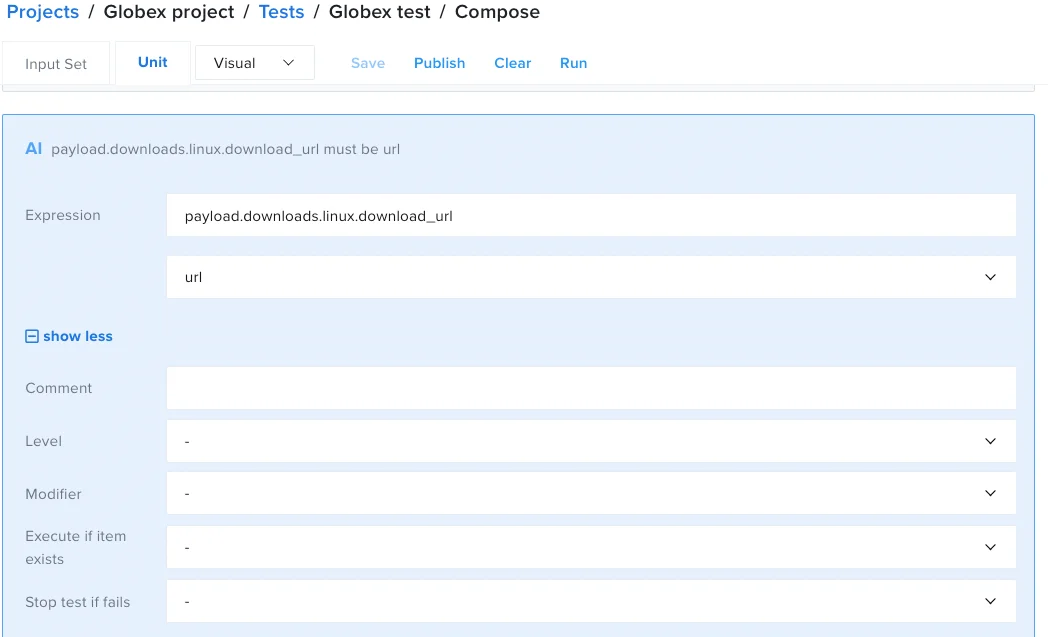
- The result should look like the following:

Run the Test
In the Composer, click Run.
All test runs appear to the right of the Composer, under the test details and environment sections.
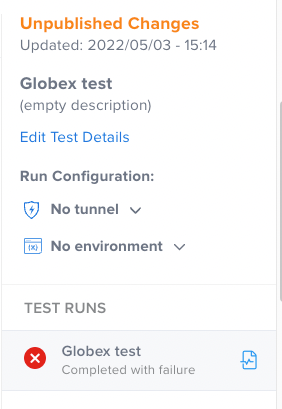
Review Test Results
To view your results, in the Composer, in the Test Runs list, click the name of the test. This will open the Test Report Details. For more information, see Test Outcome Report.
Edit a Test
To edit a test at any time, on the Projects page, on the Tests screen, hover over a test name and then click Edit Test.
Test Options
Once you've generated your tests in the Composer, you can manage them from the Tests screen. In your project, on the Tests screen, hover your mouse over the test line item. You'll see icons that allow you to edit, run, schedule, or delete a test.
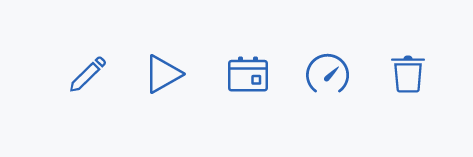
- Pencil icon: Edit the test (opens the Compose tab)
- Play icon: Run the test manually
- Calendar icon: Open the test scheduler
- Gauge icon: Opens the load testing page
- Trash icon: Delete the test
Terminology
Visual View and Code View
This toggle switches between the Visual and Code views in the Composer. You can make calls and add assertions for testing your APIs, and insert variables wherever needed. You can use either, depending on which you're more comfortable with.
Visual View
Guides you through creating API tests using automated real-time suggestions via predictive text. No coding experience is required.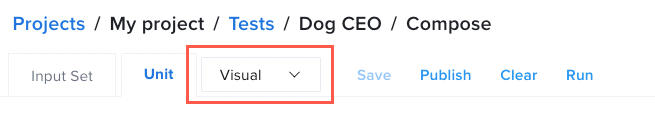
Code View
Enables you to write tests here from scratch, if you feel more comfortable working in code.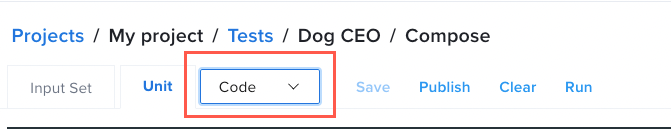
Add Child Component
This button displays all available assertion components, I/O components, and logical components.

If a component is not valid for the operation you are conducting, it will not be made available to help avoid mistakes. For instance, if you don’t add a POST first, you cannot add a POST Body or POST Param.
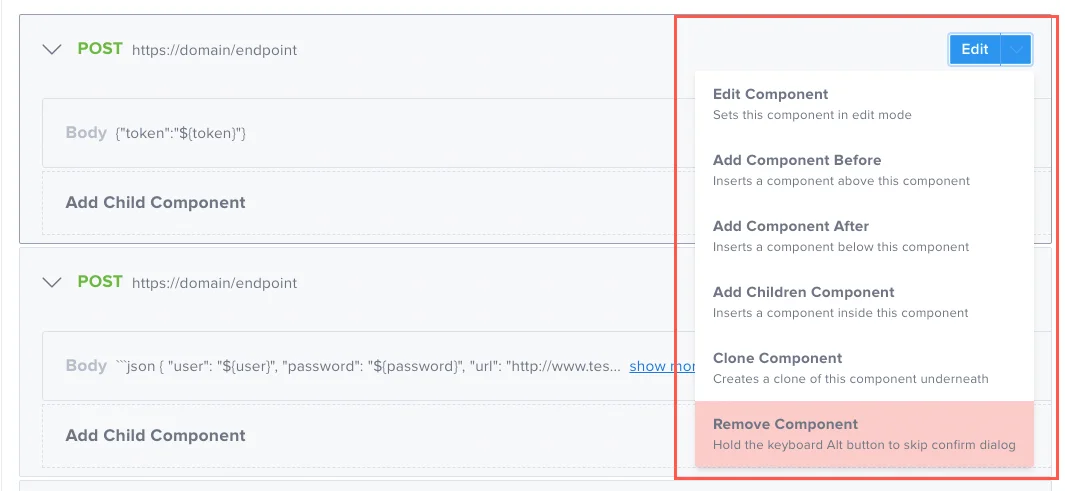
Component Options
Click Edit to modify an existing component, or use the dropdown menu next to Edit to perform the actions shown below.
Save
Saves your progress.

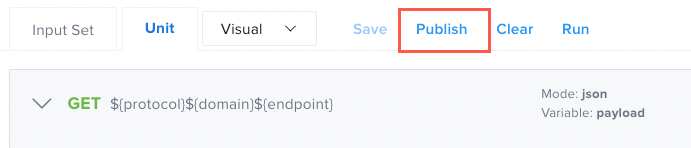
Publish
Publishes your test.
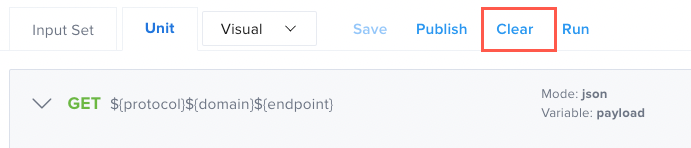
Clear
Clears the most recent unpublished changes made to your test.
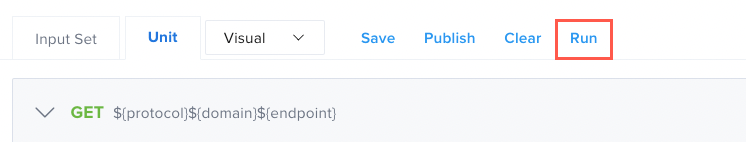
Run
Executes a test.
Input Sets
Displays the Input Set view where you can store input data sets to reuse within the specific test you're working on.
There are two types of input data sets you can use:
- Global Parameters - Variables that are specific to the test but are not related to a specific scenario (for example, api key).
- Input Set - Group of input variables representing a scenario, valid for that specific test only. The test will be executed once for each input set, overriding the variable values into your test.
If you define a variable in both the Global Parameters and Input Set sections, the value used in the test is what you specified in the Input Set.
| Input Set with Visual View | 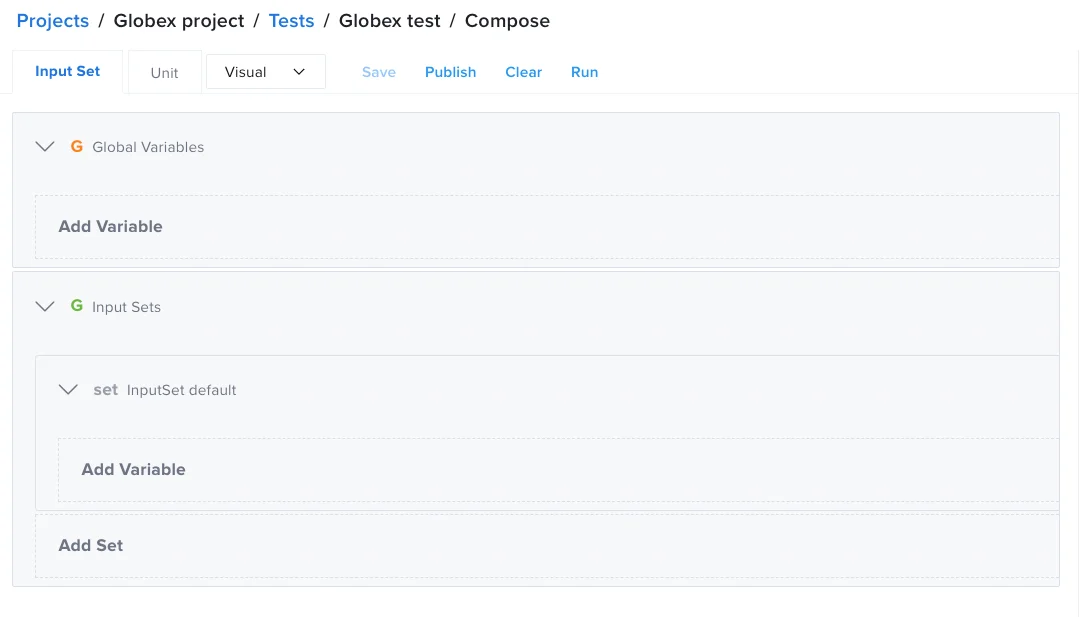 |
| Input Set with Code View | 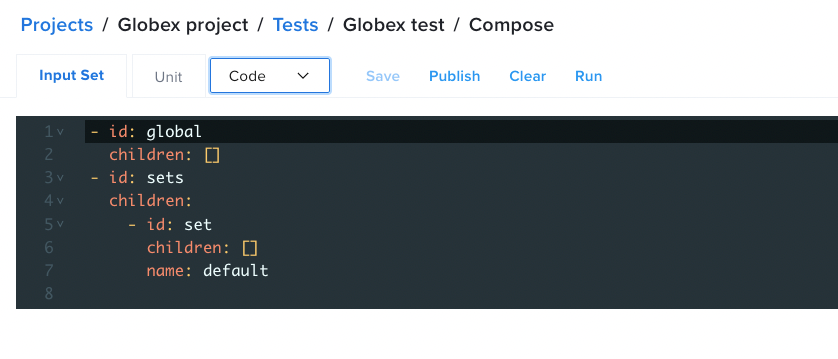 |
Unit View
These buttons switch between the Input Set and Unit views.
More Information
- API Testing Quickstart
- Check our Use Cases out to see practical examples to help you write your tests.