Different ways to set a variable
The SET (Variable) component allows you to create variables from a string to a payload. In this guide, you will learn about the various ways to create a variable.
What You'll Need
- A Sauce Labs account (Log in or sign up for a free trial license).
- An existing API Testing Project. For details on how to create one, see API Testing Quickstart.
- Familiarity with the API Testing Composer.
Mode: String
This mode generates a String variable, which can be a static value or a variable taken from the response payload. If it is a static value you just have to write it and the engine will take it as is.
Consider the following example:

- id: set
var: product
mode: string
value: t-shirt
In the above example the variable product will always have the value t-shirt.
If you write it in ${...} brackets, you will make it dynamic and let the engine evaluate the value every time the test will be executed.
Consider the following response payload that has been stored in the payload variable:
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Baseball Cap",
"price": 29.99,
"category": "1",
"description": "This is product 1!",
"quantity": 5,
"imageURL": "http://image.com",
"color": [
"blue",
"yellow"
],
"createdAt": "2021-11-28T21:58:43.461Z",
"updatedAt": "2021-11-28T21:58:43.461Z"
}
If you write the following:
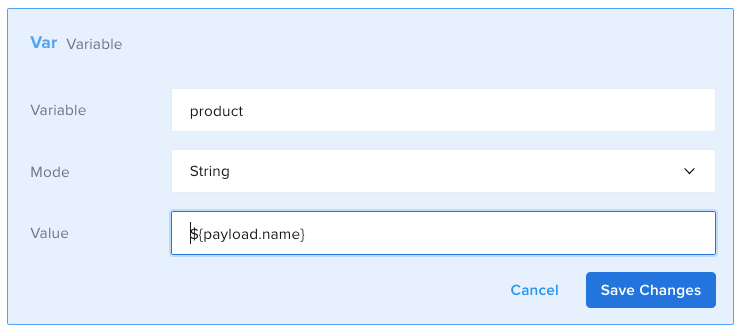
- id: set
var: product
mode: string
value: ${payload.name}
The engine will evaluate the variable value every time the test will be executed. In the above scenario the variable product will contain the value Baseball Cap but if the response is the following:
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Long Sleeve Shirt",
"price": 39.99,
"category": "1",
"description": "This is product 2!",
"quantity": 7,
"imageURL": "http://image.com",
"color": [
"blue",
"yellow",
"red"
],
"createdAt": "2021-11-28T21:58:43.461Z",
"updatedAt": "2021-11-28T21:58:43.461Z"
}
The value will be Long Sleeve Shirt, without changing your test.
Mode: Data
Using this mode, the variable will be evaluated (as an Expression field), therefore the variable type can be any type. The variable type will depend on the object being evaluated. In the Data field, you need to enter a single line expression that returns a value.
For example, you can create a new array in this way:
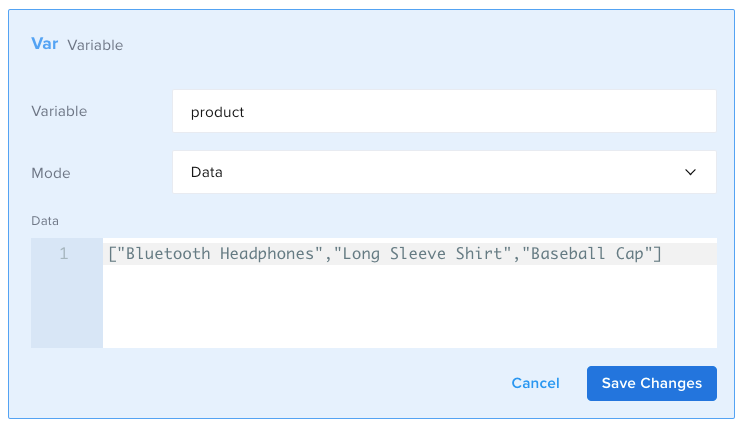
- id: set
var: product
mode: object
object: '["Bluetooth Headphones","Long Sleeve Shirt","Baseball Cap"]'
Then, you can iterate over it using the each component, or you can invoke a specific item using ${product[1]} where the number inside the square brackets identifies the position of the object you want to call, starting from 0.
Next, consider the example below where the JSON payload is stored in the payload variable:
[
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Baseball Cap",
"price": 29.99,
"category": "1",
"description": "This is product 1!",
"quantity": 5,
"imageURL": "http://image.com",
"color": [
"blue",
"yellow"
],
"createdAt": "2021-11-28T21:58:43.461Z",
"updatedAt": "2021-11-28T21:58:43.461Z"
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Long Sleeve Shirt",
"price": 39.99,
"category": "1",
"description": "This is product 2!",
"quantity": 7,
"imageURL": "http://image.com",
"color": [
"blue",
"yellow",
"red"
],
"createdAt": "2021-11-28T21:58:43.461Z",
"updatedAt": "2021-11-28T21:58:43.461Z"
},
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Bluetooth Headphones",
"price": 49.99,
"category": "1",
"description": "This is product 3!",
"quantity": 50,
"imageURL": "http://image.com",
"color": [
"green",
"yellow"
],
"createdAt": "2021-11-28T21:58:43.462Z",
"updatedAt": "2021-11-28T21:58:43.462Z"
}
]
If you write the following:
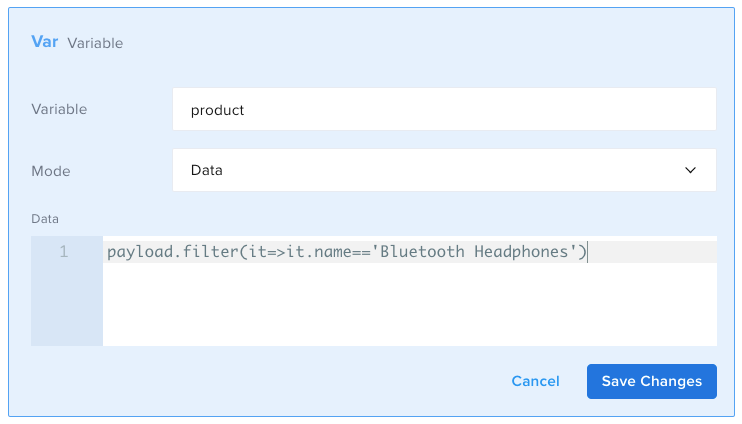
- id: set
var: product
mode: object
object: payload.filter(it=>it.name=='Bluetooth Headphones')
It will return the following object:
{
"id": 3,
"name": "Bluetooth Headphones",
"price": 49.99,
"category": "1",
"description": "This is product 3!",
"quantity": 50,
"imageURL": "http://image.com",
"color": [
"green",
"yellow"
],
"createdAt": "2021-11-28T21:58:43.462Z",
"updatedAt": "2021-11-28T21:58:43.462Z"
}
Mode: Language
This mode is the most advanced way to create your variables. The available options are: Javascript and Template.
Lang: Javascript
In this mode you can create your variable by writing a JavaScript script in the Body field. It can be a complete script with variable declarations or loops.
For example, you have a JSON Web Token (JWT) token stored in the token variable and you need to decode it and return the JSON payload it was generated from:
eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpYXQiOjE2NTgyMzY1NjgsImV4cCI6MTY4OTc3MjU2OCwiYXVkIjoid3d3LmV4YW1wbGUuY29tIiwic3ViIjoiam9obi5kb2VAZXhhbXBsZS5jb20iLCJOYW1lIjoiSm9obiIsIlN1cm5hbWUiOiJEb2UiLCJFbWFpbCI6ImpvaG4uZG9lQGV4YW1wbGUuY29tIiwiUm9sZSI6WyJNYW5hZ2VyIiwiUHJvamVjdCBBZG1pbmlzdHJhdG9yIl19.DN7vKPlHkAy1hwYOYpUKDwkV0yD-KS2pdoc76aKPhm8
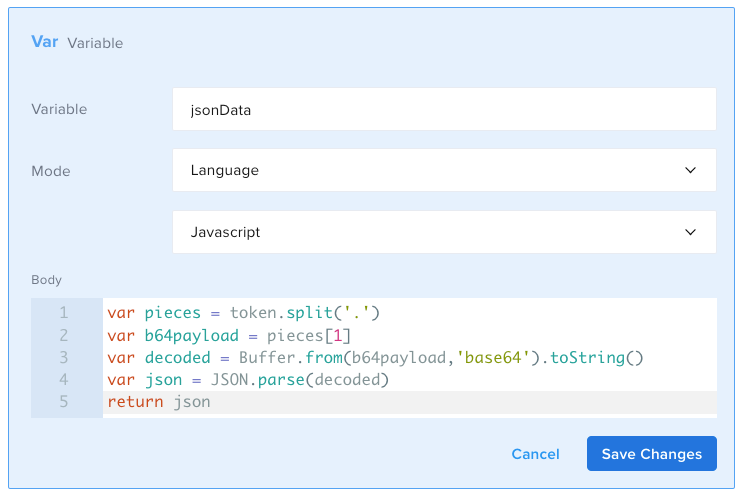
To do so, you need to write the following script inside the Body field:
var pieces = token.split('.')
var b64payload = pieces[1]
var decoded = Buffer.from(b64payload, 'base64').toString()
var json = JSON.parse(decoded)
return json
That will produce the following JSON:
{
"iat": 1658236568,
"exp": 1689772568,
"aud": "www.example.com",
"sub": "john.doe@example.com",
"Name": "John",
"Surname": "Doe",
"Email": "john.doe@example.com",
"Role": [
"Manager",
"Project Administrator"
]
}
Then, you can retrieve all the keys as jsonData.iat where jsonData is the variable name you entered in the Variable field.
Lang: Template
In this mode, you can create your own template in the same way as it is done for Request Body, the advantage here is that you can print the variable to check if all is correct (Body cannot be printed).
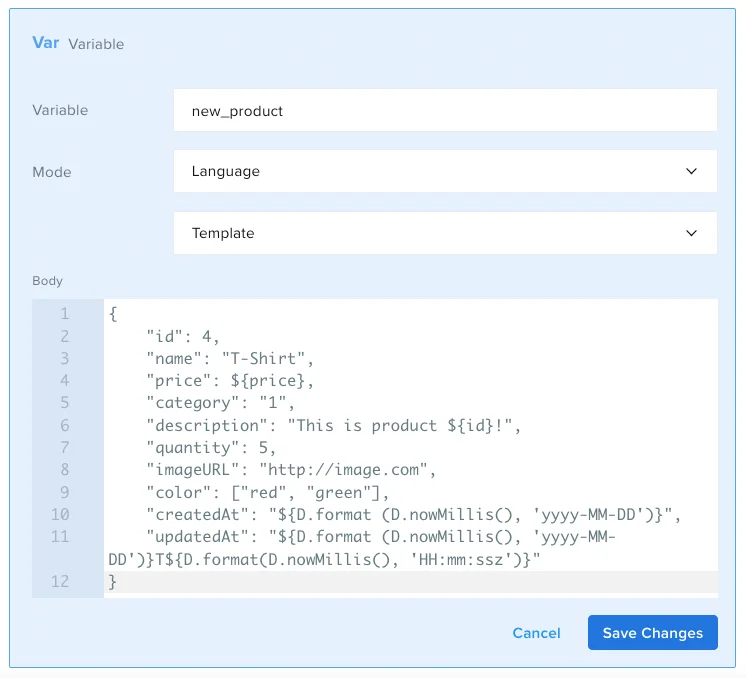
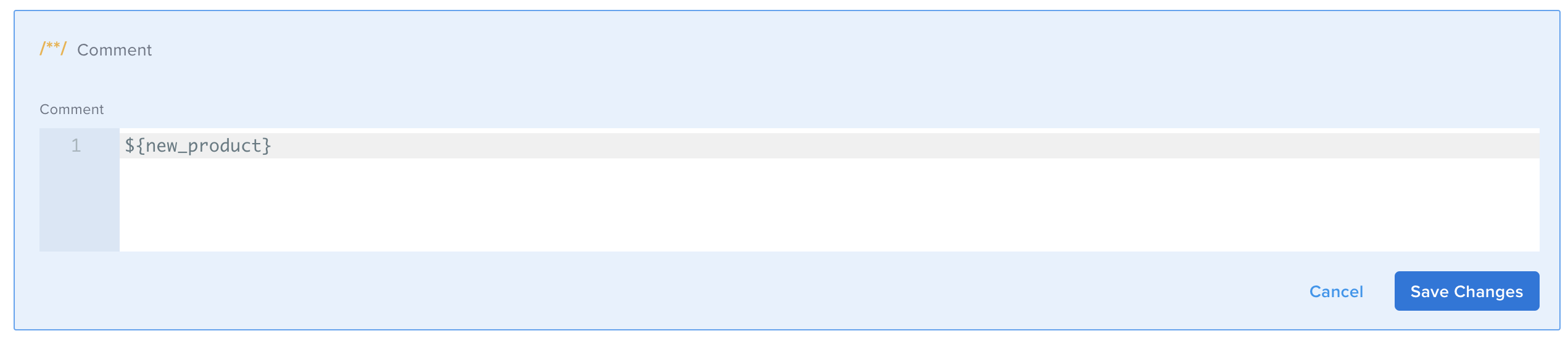
For example, if you need to add a new product to your database, you can create the body for the (PUT) request and paste it in the Body field, and then print it in a Comment.
{
"id": 4,
"name": "T-Shirt",
"price": ${price},
"category": "1",
"description": "This is product ${id}!",
"quantity": 5,
"imageURL": "http://image.com",
"color": ["red", "green"],
"createdAt": "${D.format (D.nowMillis(), 'yyyy-MM-DD')}",
"updatedAt": "${D.format (D.nowMillis(), 'yyyy-MM-DD')}T${D.format(D.nowMillis(), 'HH:mm:ssz')}"
}